how does a circuit breaker work gcse
Residual Current Circuit Breaker - RCCB. Each breaker is connected to an electrical wire that runs through your house.
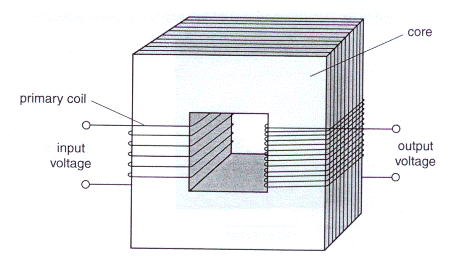
Gcse Science Physics Past Paper J03 2
How does a fuse work GCSE.

. Touch device users explore by touch or with swipe gestures. The fuse which contains a piece of wire that melts easily if the current going through it is too great breaks the circuit if a fault in an appliance. Inside each circuit breaker is a spring hooked over a small piece of solder a melt-able fusible alloy.
When autocomplete results are available use up and down arrows to review and enter to select. What are circuit breakers and how do they work. This tutorial explains how a residual current circuit breaker works and its advantages compared to traditional fusesSubscribe for more physics tutorials.
How does a circuit breaker work GCSE electromagnet. For protection against faults of this nature a circuit-breaker is used in place of a fuse. Residual Current Circuit Breakers have the advantage of being highly.
How does a Residual Current Circuit Breaker Work. The air circuit breaker is also known as an air blast circuit breaker as they are air-based circuit breakers. The two magnetic fields do not cancel each other out and the iron pivot is attracted to the live wire breaking the circuit.
The charging current can be limited to 15 A using a fuse or a circuit breaker 1. A circuit breaker would be better than a fuse since a fuse would need to be replaced after use 1. Circuit-breakers offer the following advantages compared to fuses.
A circuit breaker is an automatic switch that cut off current in a circuit when the current become too large. In this circuit breaker type the arc extinguishing medium used. An RCCB is also called an RCD Residual Current Device.
A circuit breaker is an electrical device used in an electrical panel that monitors and controls the amount of amperes amps.

How Circuit Breakers Work Simply Explained Bay Power
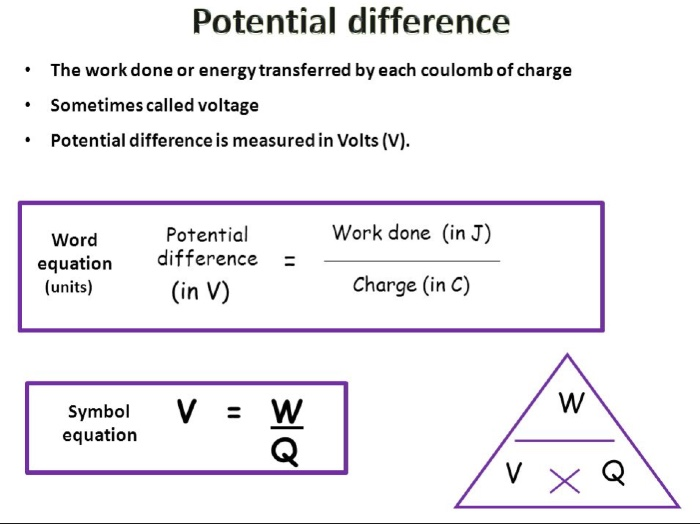
Gcse Physics Electricity Flashcards Chegg Com

Advantages Disadvantages Of Circuit Breakers Fuses Hunker

Magnetism And Electromagnetism Edexcel I Gcse Physics Magnets

Electrical Safety 2 3 3 Edexcel Igcse Physics Revision Notes 2019 Save My Exams

Controlling Current In Electric Circuits Ck 12 Foundation

Gcse Aqa Physics Complete Study Notes Physics Higher Gcse Aqa Thinkswap

Electricity And Magnetism Circuit Breakers Reed Switches Gcse Physics Youtube

Electrical Safety 2 3 3 Edexcel Igcse Physics Revision Notes 2019 Save My Exams

Key Differences Between Fuses And Circuit Breakers Steiner Electric Company Blog
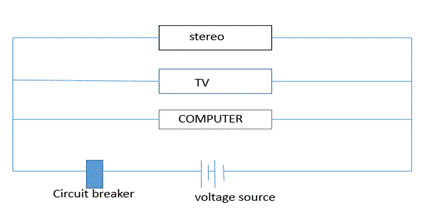
To Draw A Circuit Diagram Showing The Way That A Stereo A Tv And A Computer Can Be Connected To A Single Source Of Voltage Difference Such That Turning Off One Appliance

New Gcse Add L Science Ocr Gateway Sb Page 240

Uses Of Electromagnet Circuit Breaker Spm Physics Form 4 Form 5 Revision Notes

New Gcse Add L Science Ocr Gateway Sb Page 240
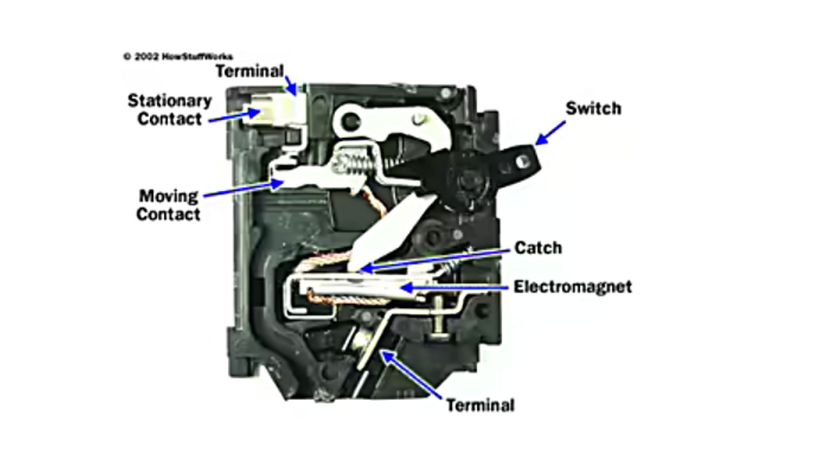
How Circuit Breakers Work Howstuffworks
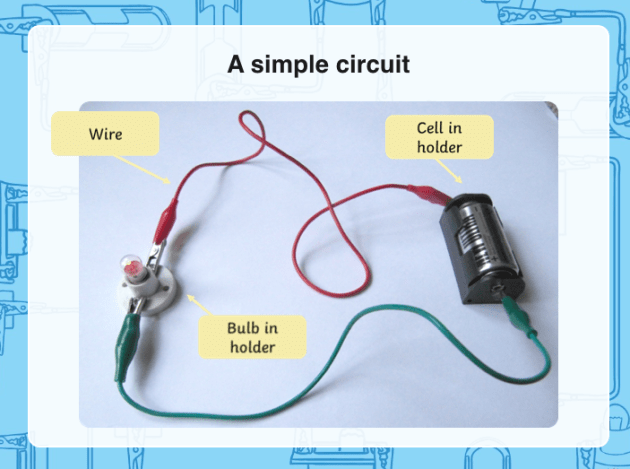
What Is A Series Circuit Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki

Electrical Safety 2 3 3 Edexcel Igcse Physics Revision Notes 2019 Save My Exams

Gcse Ocr 21st Century Physics Electric Circuits Complete Revision Summary Expert Guidance By Mahima Laroyia

Electromagnets In Devices Electromagnetism Physics Year 11 Gcses Diagram Quizlet